Pneumatic vs. Electric Nailer: How to Choose the Best Option for Your Workflow
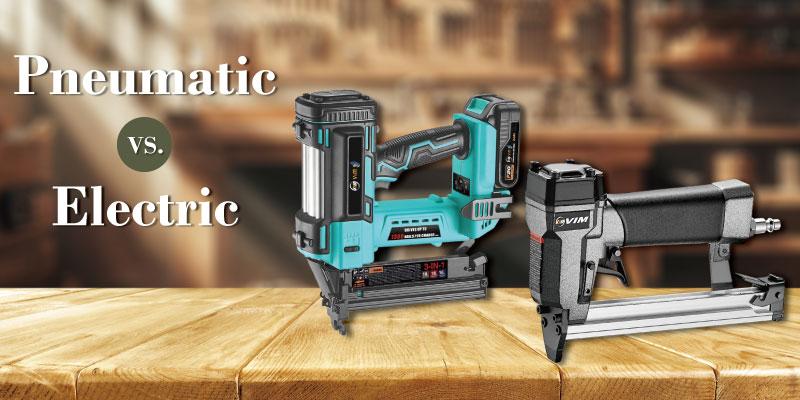

Choosing between a pneumatic nailer and an electric nailer is a common challenge for professionals and DIY users alike. While both tools are designed for fastening applications, they differ significantly in power source, performance, cost, and ideal usage scenarios. Understanding these differences can help you avoid unnecessary investment and select the nailer that best fits your workflow. This article compares pneumatic and electric nailers, covering key features, applications, and practical factors to consider before making a decision.
What is a Pneumatic Nailer?
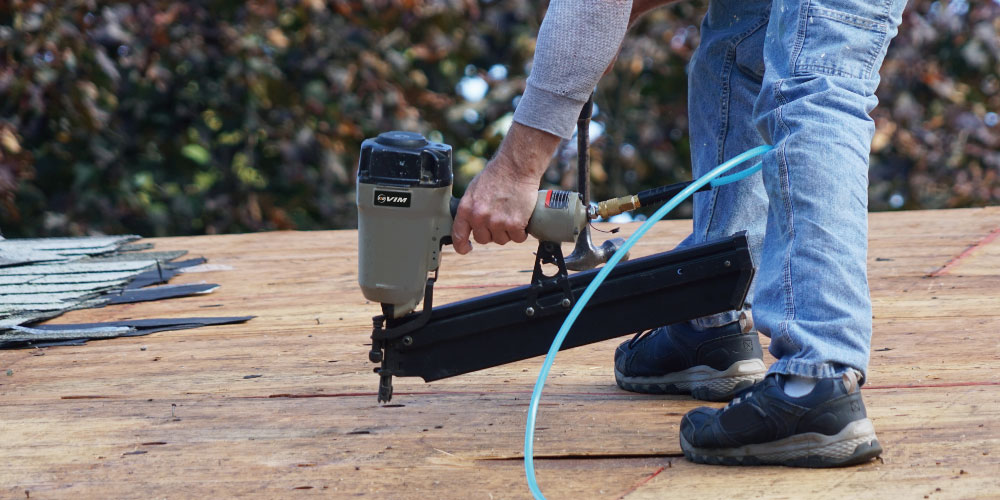

A pneumatic nailer is an air tool that uses compressed air from an external air compressor to drive nails into various materials, such as wood. When the rigger is pulled, compressed air pushes an internal piston, delivering the force needed to drive the nail accurately and efficiently.
Pneumatic nailers are commonly used in construction, woodworking, and industrial applications where consistent air-powered operation is required. They are designed to work as part of a compressed air system, making them a standard tool in professional work.
【Related products: Air Nailer】
What is an Electric Nailer?
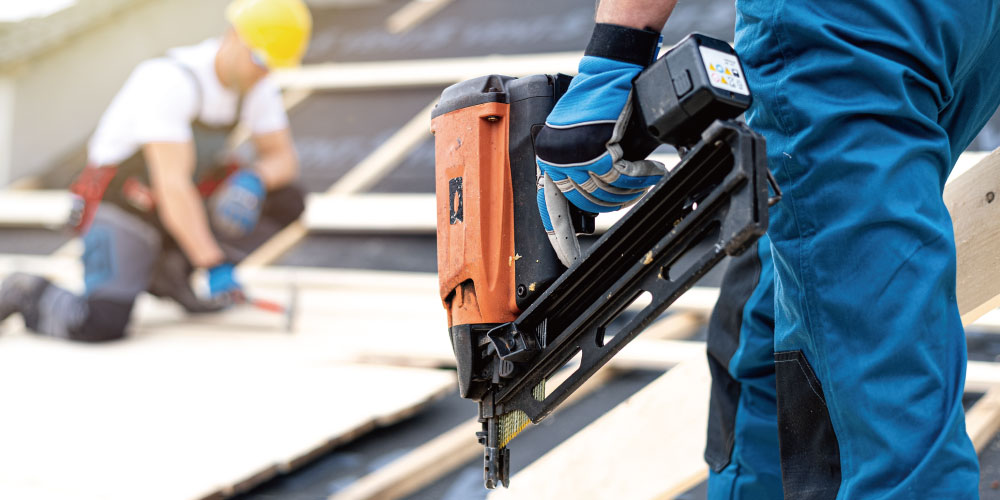

An electric nailer is a nail-driving tool powered by electricity, either through a power cord or built-in rechargeable battery. It uses an internal motor or drive mechanism to deliver the force needed to fasten nails into wood and other materials.
Because it operates as a standalone tool, an electric nailer is often used in applications where mobility, quick setup, or limited workspace is important. It is commonly found in home improvement projects, interior finishing, and light-duty woodworking tasks where a compact and self-contained solution is preferred.
【Extending reading: What Happens When a Driver Blade Fails? Lessons from the Paslode 901078】
Key Differences Between Pneumatic Nailer and Electric Nailer
Understanding the differences between a pneumatic nailer and an electric nailer helps evaluate which fastening solution best fits your working environment, performance requirements, and long-term usage needs.
Power Source & Operating Mechanism
A pneumatic nailer is an air tool by compressed air supplied from an external air compressor. The driving force is generated through air pressure acting on an internal piston, which delivers consistent mechanical energy for nail fastening.
An electric nailer operates using electricity, either through a power cord or a rechargeable battery. It relies on an internal motor or spring-driven mechanism to generate driving force, eliminating the need for an external air supply.
【Extending reading: Nail Gun Leaking Air from Trigger? Step-by-Step Fix & Prevention】
Portability & Setup Requirements
Pneumatic nailers require a supporting air system, including an air compressor, air hose, and pressure regulation. This setup can limit portability but is commonly integrated into professional work environments where multiple air tools are already in use.
Electric nailers are generally more portable due to their self-contained design. With no air hose or compressor required, they allow for faster setup and easier movement between work areas, particularly in smaller or enclosed spaces.
【Extending reading: Maximize Tool Performance: 4 Smart Ways to Pick the Best Air Tool Fittings】
Fastening Speed & Performance Consistency
Pneumatic nailers are known for stable and repeatable fastening performance, as air pressure can be precisely regulated. This makes them suitable for applications involving continuous operation or high fastening frequency.
Electric nailers provide reliable performance for intermittent or moderate workloads. However, fastening speed and consistency may vary depending on battery capacity, motor output, or power supply conditions.
【Extending reading: The All-in-One Reference for 4 Firing Modes in Pneumatic Tools】
Tool Weight & Ergonomics
Because the power source of a pneumatic nailer is external, the tool itself is often lighter and well balanced. This can reduce user fatigue during extended operation, especially in repetitive fastening tasks.
Electric nailers integrate the motor and power components within the tool body, which can increase overall weight. Advances in battery and motor design have improved ergonomics, but weight distribution may still vary by model and application.
Application Range & Material Compatibility
Pneumatic nailers are widely used across construction, woodworking, packaging, and industrial manufacturing. Their compatibility with various nail sizes and materials makes them suitable for both light-duty and heavy-duty applications.
Electric nailers are commonly applied in home improvement, interior finishing, and light construction work. They are typically designed for specific fastening ranges and may be optimized for softer materials or controlled environments.
【Extending reading: Everyone Needs to Know the Complete Guide to Wide Crown Staplers】
Cost & Long-Term Investment
In general, the initial purchase price of a pneumatic nailer is often lower than that of an electric nailer. However, pneumatic systems may require additional investment in supporting equipment such as air compressors, air hoses, and air preparation units. In work environments where air tools are already in place, this infrastructure cost is typically shared across multiple tools.
Electric nailers usually involve a higher unit cost due to built-in motors and battery systems, while requiring little to no external equipment. When evaluating long-term investment, factors such as battery and charger replacement, battery lifespan, charging downtime, and overall tool durability should be considered alongside the initial purchase price, as batteries and chargers typically have a shorter service life and need to be replaced periodically.
Pneumatic Nailer vs Electric Nailer: Quick Comparison
| Factor | Pneumatic Nailer | Electric Nailer |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Compressed air | Electricity (cord or battery) |
| Setup | Compressor & hose required | No external equipment |
| Portability | Limited | High |
| Fastening Speed | Consistent, high-frequency use | Moderate, battery-dependent |
| Tool Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Applications | ‧ Industrial ‧ Construction ‧ Heavy-duty |
‧ Home ‧ Interior ‧ Light-duty |
| Cost | ‧ Lower tool cost ‧ Share air system |
‧ Higher unit cost ‧ Battery replacement |
How to Choose Between Pneumatic Nailer and Electric Nailer

Choosing between a pneumatic nailer and an electric nailer depends on your working environment, usage frequency, application scale, and long-term operational needs. Rather than focusing on a single feature, it is important to evaluate how each tool fits into your overall workflow.
A pneumatic nailer is ideal for professional woodworking, industrial production, and high-volume manufacturing. With a generally lower initial tool cost and the ability to integrate into existing air systems, pneumatic nailers offer fast, consistent, and high-quality fastening. They are especially suitable for long-term, repetitive use where stable performance is essential.
An electric nailer, on the other hand, is better suited for smaller-scale projects, home improvement, or DIY use. Its self-contained design makes it convenient for indoor work and areas with limited space, but the overall investment per tool is higher, Electric nailers are less practical when multiple units are required simultaneously, as their higher unit cost and battery maintenance make large-scale deployments less efficient.
Ultimately, the choice comes down to your workflow, usage needs, and budget. Pneumatic nailers are ideal for high-volume, professional use, while electric nailers offer convenience and flexibility for smaller projects or indoor work.
【Extending reading: All You Need to Know to Choose Your Perfect Air Nailers, Air Staple Guns, and Air Pliers】
Explore VIM’s Pneumatic Nailer Range

After understanding the differences between pneumatic and electric nailers, many professionals choose pneumatic tools for high-volume or industrial applications. To meet these needs, VIM provides a wide range of high-quality pneumatic nailers engineered for durability, consistent performance, and efficiency. Our tools integrate seamlessly into existing air tool systems, making them suitable for workshops, construction sites, and large-scale production.
Available Pneumatic Nailer Types:
- Pin Nailer
- Coil Nailer
- Finishing Nailer
- Corrugated Nailer
- Concrete Nailer
- Framing Nailer
- Plastic Cap Nailer
- Frame Nailer
- Decorative Nailer
Whether you need a single unit for specialized tasks or multiple tools for industrial operations, VIM’s pneumatic nailers offer reliable performance and long-term value.
【Extending reading: Air Pinner Buying Guide - 6 Points to Distinguish Air Pinner and Finishing Nailer】
Conclusion
Selecting between a pneumatic nailer and an electric nailer ultimately depends on your workflow, project scale, and long-term requirements. Pneumatic nailers are well-suited for high-volume, professional, and industrial use, offering consistent performance, fast fastening, and cost efficiency when integrated into air tool systems. Electric nailers provide portability, convenience, and flexibility for smaller projects, indoor work, or DIY applications, though they may involve higher per-unit costs and battery maintenance. By evaluating performance, portability, and total ownership costs, users can make an informed choice that aligns with their specific application and operational needs.
If you are looking for high-quality professional pneumatic nailers, feel free to contact us for more information. Our team will be happy to provide product details, technical support, and quotations to help you identify the most suitable solution for your requirements.
Article Classification
Recent Articles
- Pneumatic vs. Electric Nailer: How to Choose the Best Option for Your Workflow
- Avoid Costly Jams: 5 Proven Hog Ring Plier Repair Solutions that Work
- 4 Simple Ways to Maintain Your Hog Ring Plier for Better Performance
- Narrow vs Wide Crown Stapler: 3 Steps to Make the Right Choice
- Safety Starts Here: Explore 5 Smart Safety Designs in Pneumatic Nailers and Staplers

